
Introduction
We’ll delve into the significance of Gums Healthy and understand why it’s an essential component of your overall oral health. We’ll also clarify the purpose of this guide and give you a sneak peek at the valuable information it holds.
The Significance of Gums Healthy
Your gums are the unsung heroes of your oral health. They play a pivotal role in not only protecting your teeth but also maintaining your overall well-being. Healthy gums are the foundation of a confident smile, and they perform several crucial functions:
- Supporting Teeth: Gums hold your teeth firmly in place. They provide a stable base for your pearly whites to chew, bite, and function effectively.
- Protecting Tooth Roots: Gums cover and protect the sensitive roots of your teeth. This keeps them safe from external factors.
- Defending Against Infections: Healthy gums act as a barrier against harmful bacteria that can lead to gum disease and other oral infections.
- Enhancing Aesthetics: Well-maintained gums contribute to an attractive smile, complementing your teeth.
- Improving Overall Health: Emerging research shows a link between gum health and systemic health. Your gums’ state can influence your body’s overall well-being.
The Purpose of this Guide
This comprehensive guide is designed to equip you with the knowledge and tools to maintain healthy gums throughout your life. Gum health is not only about preventing issues but also enhancing your quality of life.
The purpose of this guide is two-fold:
- Education: We aim to provide you with a wealth of knowledge on healthy gums, starting with understanding the basics of gum anatomy, common problems, and the role of nutrition.
- Action: We want to empower you to take control of your gum health through effective oral hygiene practices, home remedies, and regular dental check-ups.
By the end of this guide, you’ll have the insights and strategies needed to ensure your gums healthy and strong, allowing you to enjoy a confident smile and overall well-being. So, let’s embark on this journey to healthy gums together.
Understanding Gum Anatomy
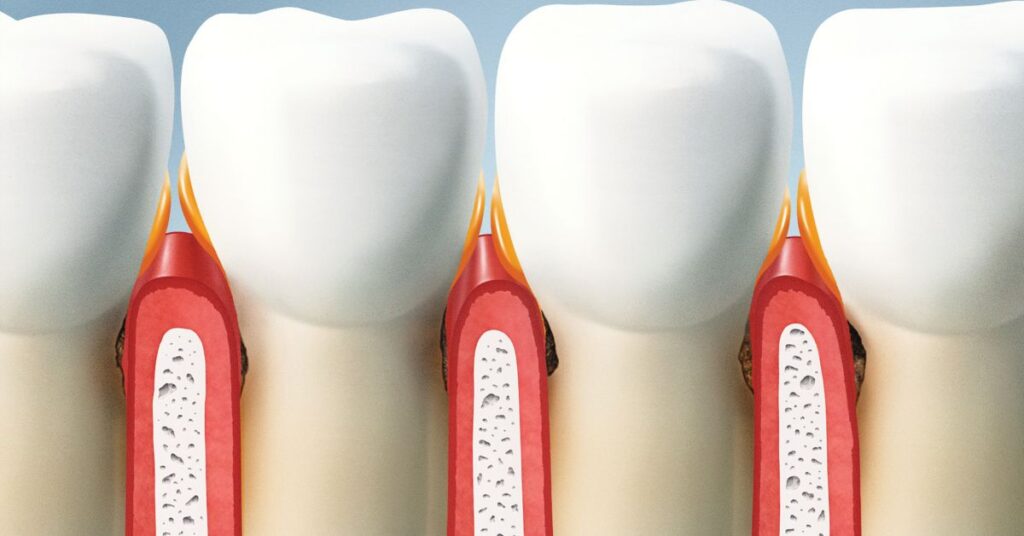
The Basics of Gum Structure
To comprehend how to maintain healthy gums, it’s essential to begin with understanding the fundamentals of gum anatomy. Your gums, also known as gingiva, are soft mucosal tissue that lines your mouth’s oral cavity. Here’s a simple overview of the structure and functions of gum tissue:
- Gingiva Types: There are two main types of gums in your mouth. The first is the keratinized gingiva, which includes the firm, dense gum tissue that covers the bony structure of your upper and lower jaws. The second is the mucosal gingiva, which is the soft and movable tissue located closer to the inside of your mouth.
- Protective Barrier: Your gums serve as a protective barrier against bacteria and irritants. They help to keep foreign substances from entering your body through the mouth.
- Sensory Function: Gums contain a rich supply of nerves, making them highly sensitive. This sensitivity helps you avoid biting down too hard or causing injury when chewing.
- Attachment Points: Gums provide an attachment point for your teeth. The firm, keratinized gingiva fuses with the tooth roots, ensuring stability.
- Maintaining Tooth Position: Your gums play a crucial role in maintaining the position of your teeth in your mouth. Healthy gums ensure your teeth remain securely in place.
The Gum-tooth Interface
The connection between your gums and teeth is a critical one. This gum-tooth interface, often referred to as the gum line, is where your gums adhere to the surfaces of your teeth. Understanding this connection is vital for maintaining good oral health:
- Sealing Gap: Your gums seal the gap between your teeth and their roots. This seal prevents bacteria from reaching the more vulnerable parts of your teeth.
- Aesthetics: The gum line also plays a significant role in the aesthetics of your smile. When it is even and symmetrical, it contributes to a pleasing appearance.
- Exposing Tooth Roots: In cases of gum recession, the gum line recedes, potentially exposing the tooth roots. This can lead to increased sensitivity and other oral health concerns.
- Gingival Health: The state of your gums, particularly the gum line, can be a good indicator of overall gum health. Healthy gums are typically pink, firm, and do not bleed easily.
Understanding the structure and function of your gums lays the foundation for effective gum care. The next chapters will explore common gum issues, the role of nutrition in gum health, and tips for maintaining strong and healthy gums throughout your life.
Common Gum Problems
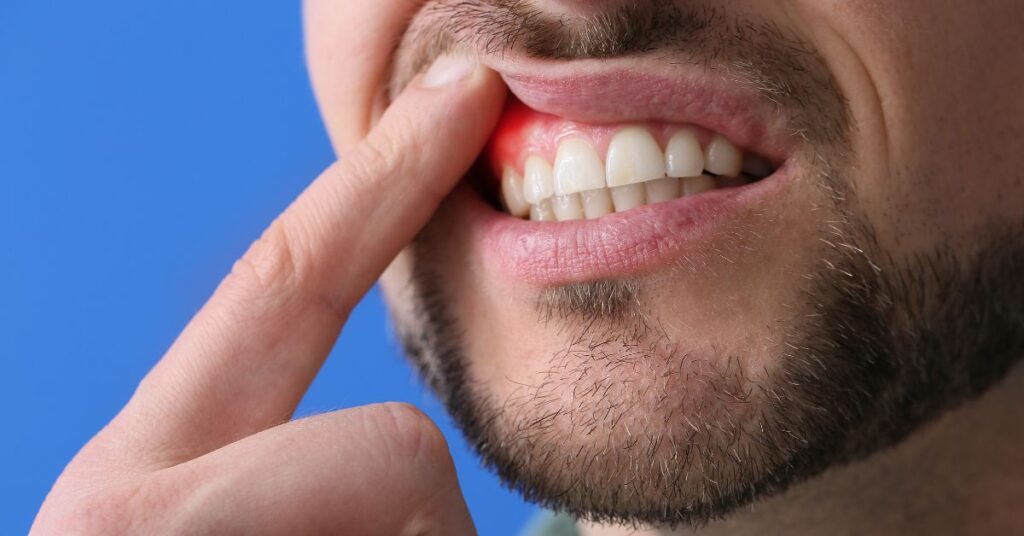

Gums healthy is not something to be taken lightly. It forms the foundation of your overall oral well-being, and when issues arise, they can lead to a range of dental problems. In this chapter, we will delve into common gum problems, their causes, and the symptoms to watch out for.
Gum Disease: Causes and Symptoms
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a prevalent issue that affects countless individuals. It occurs when bacteria in your mouth combine with mucus and food particles, forming plaque on your teeth. Here are the key aspects of gum disease you should be aware of:
Causes of Gum Disease:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Failing to brush and floss regularly can lead to plaque buildup.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use: Tobacco is a significant contributor to gum disease.
- Diet: A diet high in sugars and carbohydrates can increase the risk of gum problems.
- Genetics: Some individuals are genetically predisposed to gum disease.
Symptoms of Gum Disease:
- Swollen Gums: Inflamed and puffy gums are an early sign.
- Bleeding Gums: Gums that bleed when you brush or floss.
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath can be an indicator.
- Receding Gums: Gums that pull away from your teeth.
- Tooth Mobility: Loose teeth can be a severe symptom of advanced gum disease.
Timely detection and intervention are essential to prevent gum disease from advancing. Regular dental check-ups are vital for monitoring your gum health and catching any issues early on.
Gum Recession: Causes and Risks
Gum recession is another prevalent concern related to gum health. It occurs when the margin of the gum tissue surrounding the teeth pulls back or wears away, exposing more of the tooth, or its root. Let’s explore the reasons behind gum recession and the risks associated with it:
Causes of Gum Recession:
- Aggressive Brushing: Brushing your teeth too vigorously can erode gum tissue.
- Periodontal Disease: Advanced gum disease can lead to gum recession.
- Genetics: Some people have a genetic predisposition to receding gums.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations can make gums more sensitive.
Risks of Gum Recession:
- Tooth Sensitivity: Exposed roots can lead to increased tooth sensitivity.
- Aesthetics: Gum recession can affect the appearance of your smile.
- Tooth Mobility: Severe recession may cause tooth mobility.
- Root Decay: Exposed roots are more prone to decay.
The Role of Nutrition in Gum Health

When it comes to maintaining healthy gums, a well-balanced diet can be your ally. In this chapter, we will explore the crucial role that nutrition plays in gum health, the essential nutrients you need, and the foods to embrace or avoid.
A Balanced Diet for Gums Healthy
A diet that promotes healthy gums is also one that promotes overall well-being. Here’s what you need to know about building a gum-friendly diet:
Essential Nutrients for Gum Health:
- Vitamin C: This vitamin is crucial for collagen production, which is essential for gum tissue strength. Find it in citrus fruits, strawberries, and broccoli.
- Vitamin D: Vitamin D helps your body absorb calcium, promoting gum and tooth health. Get your dose from fatty fish, fortified dairy, and sunlight.
- Calcium: Calcium contributes to tooth and bone health. Dairy products, leafy greens, and almonds are excellent sources.
- Vitamin A: For healthy mucous membranes and oral tissues, vitamin A is a must. Carrots, sweet potatoes, and spinach are rich in vitamin A.
- Antioxidants: These help reduce inflammation and support gum health. Berries, nuts, and whole grains are packed with antioxidants.
Foods to Avoid for Gums Healthy
While some foods can be your gum’s best friend, others can be your worst enemy. Avoiding certain items can help protect your gum health:
Sugary Foods and Beverages: Sugars provide a feast for harmful bacteria in your mouth, leading to plaque and gum problems. Limit sugary treats and beverages.
Acidic Foods: Highly acidic foods can erode tooth enamel and irritate your gums. Citrus fruits, vinegar, and carbonated drinks should be consumed in moderation.
Smoking and Tobacco: Tobacco use is a significant risk factor for gum disease. It not only stains your teeth but also hampers blood flow to the gums.
Your diet’s impact on your gum health cannot be overstated. By embracing nutrient-rich foods and steering clear of those that harm your gums, you’re taking a significant step toward maintaining a confident and healthy smile. In the following chapters, we’ll explore effective oral hygiene practices and home remedies for gum care.
Effective Oral Hygiene Practices
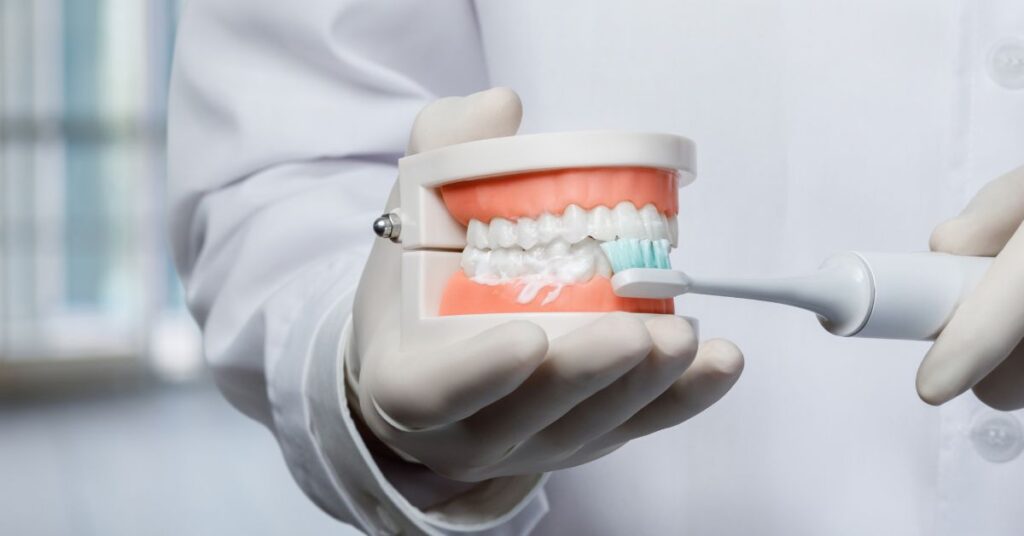
Achieving and maintaining healthy gums isn’t just about what you eat; it’s also about how you care for your oral hygiene. In this chapter, we delve into the essentials of effective oral hygiene practices that are instrumental in safeguarding your gum health.
The Basics of Gum Care
Brushing Techniques for Gums Healthy
Proper brushing is your first line of defense against gum problems. Here’s how to do it right:
- Brush Twice Daily: Aim to brush your teeth at least twice a day, ideally in the morning and before bedtime.
- Choose the Right Toothbrush: Opt for a soft-bristle toothbrush to avoid damaging your gums. Make sure to replace your toothbrush every three to four months.
- Use Fluoride Toothpaste: Fluoride helps strengthen your teeth and prevents decay. Ensure your toothpaste contains fluoride.
- Brush Gently: Don’t brush aggressively; this can harm your gums. Instead, use gentle circular motions.
Flossing for Healthy Gums
Flossing is the unsung hero of gum care. It helps remove plaque and debris between teeth that your toothbrush can’t reach. Here’s how to floss effectively:
- Floss Once a Day: Commit to daily flossing, usually before bedtime.
- Be Gentle: Avoid snapping the floss between your teeth, as it can injure your gums.
- Use Enough Floss: You should use about 18 inches of floss to ensure you’re not reusing the same section.
- Embrace Dental Picks or Interdental Brushes: If traditional floss doesn’t work for you, consider dental picks or interdental brushes.
Special Considerations for Gum Health
If you have specific gum concerns, it’s essential to adapt your oral care routine to address them. Here are some tips for individuals with special gum issues:
Dealing with Gum Sensitivity
- Choose a toothbrush with ultra-soft bristles.
- Use toothpaste formulated for sensitive teeth.
- Consider an alcohol-free mouthwash.
Managing Gum Bleeding
- Don’t stop brushing or flossing if your gums bleed; this could worsen the issue.
- Focus on gentle brushing and flossing techniques.
- Consult your dentist for personalized advice.
Choosing the Right Oral Care Products
- Look for products with the American Dental Association (ADA) Seal of Acceptance.
- Consult your dentist for recommendations tailored to your specific needs.
With the right oral hygiene practices, you can significantly reduce your risk of gum problems. In the next chapter, we’ll explore home remedies that can complement your daily oral care routine.
Conclusion
Your journey to Gums Healthy starts now. Implement the tips and advice you’ve learned throughout this guide, and remember that consistent effort is key to maintaining Gums Healthy.
Take control of your oral well-being, make informed choices, and enjoy the confidence of a healthy smile. Thank you for choosing this guide as your companion in your quest for Gums Healthy. For personalized care and expert advice, visit Sri Sanjeevini Dental and take the next step towards achieving optimal gum health.
